If at a meal we have eaten a lot and the stomach cannot hold more, we are said to be “full”. In transformers, a similar situation occurs.
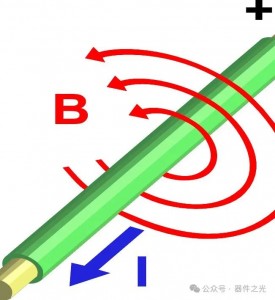
According to Ampere’s law: any wire that carries an electric current will generate a magnetic field around it. As the current (voltage) increases, the magnetic field strength will also increase, but this increase is not infinite.
When the transformer magnetic field reaches a certain level, the increase in current (voltage) cannot make the magnetic field strength continue to increase, or the increase is relatively slow, we call it “transformer magnetic saturation“.
Once magnetic saturation occurs, the transformer will not be able to continue to work normally, the mutual inductance will disappear, and the actual primary voltage ratio of the transformer will change. The secondary output voltage is no longer the voltage we require, and the output voltage waveform is distorted, which directly affects the normal operation of the product.
Secondly, the transformer can not effectively transfer energy from the primary to the secondary, and the overall transformer efficiency is reduced. When fully saturated, the transformer is equivalent to a wire, the current increases sharply, the transformer heats up quickly, and it is easy to cause the transformer to burn.
high frequency transformer manufacturers
There are many reasons for transformer magnetic saturation, generally speaking, it can be divided into four categories: 1. 2. Power grid voltage fluctuation or sudden change; 3. The power supply voltage is unstable; 4. The core is saturated.
The first three are mainly caused by external reasons, which can be solved by adjusting the load, installing the regulator, and adjusting the grid voltage. The fourth is closely related to the design of the transformer and the selection of the magnetic core, and this article focuses on it.
In a transformer, the relationship between inductance and magnetic flux can be expressed by the following formula:
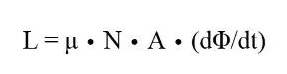
Where: L represents inductance, μ represents permeability, N represents the number of turns, A represents the effective cross-section area of the coil through the core, Φ represents magnetic flux, and t represents time.
We found that when the transformer inductance is smaller, the magnetic flux is smaller, and the less easy to saturate at this time. Therefore, the transformer can improve the anti-saturation capacity of the transformer by opening the air gap. The larger the air gap, the smaller the inductance, and the stronger the anti-saturation capacity of the transformer.
transformer ferrite core supplier
In the case of a certain amount of inductance, if the number of transformer turns is more, the magnetic flux is smaller, and the less easy to saturate at this time. In this case, the number of turns of the transformer can be appropriately increased to improve the anti-saturation capacity of the transformer.
The larger the effective cross-sectional area of the coil through the core, the less easily the transformer is saturated. We can choose a magnetic core with a larger cross-sectional area, and the corresponding magnetic core size may be larger.
The faster the rate of flux change (dΦ/dt), the higher the frequency of the transformer, we need to choose a magnetic core with lower permeability in order to improve the anti-saturation capacity of the transformer. Therefore, for high-frequency transformers, choosing the right core material is an important means to prevent transformer magnetic saturation.
The common amorphous core permeability is high, mostly in 1.0-1.7T, and the highest frequency used is 50KHz; The core conductivity of manganese zinc ferrite is between 2000 and 5000, and the frequency used can reach 100KHz; The permeability of nickel-zinc ferrite is mostly about 20~2000, and its highest operating frequency can reach MHz level.
As far as the power circuit is concerned, it can also be synchronized by setting soft start to avoid the transformer input current rising too fast, so as to avoid the purpose of magnetic saturation of the transformer.
Recommended articles:
▶ Infrared radiation alarm circuit
▶ Energy saving LED flashlight circuit
▶ Simple and practical LED light driver circuit
Post time: Dec-24-2024