Analysis of high-frequency switching power supply transformer
In the electronic products we come into contact with daily, we can find a large number of magnetic core components, among which there is the heart of the switching power supply module - the switching transformer. Nowadays, the electronic products in life have more and more stringent requirements for the appearance of ultra-small and ultra-thin products. As the heart of the energy source of these electronic products, the high-frequency switching power supply has the advantages of high efficiency, good temperature and small size. Therefore, many electronic products are high-frequency switching power supplies. As practitioners in the electronics industry, you have to know something about the transformer of the switching power supply.
The transformer is a device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to exchange current. Its main components include primary coil, secondary coil and iron core.
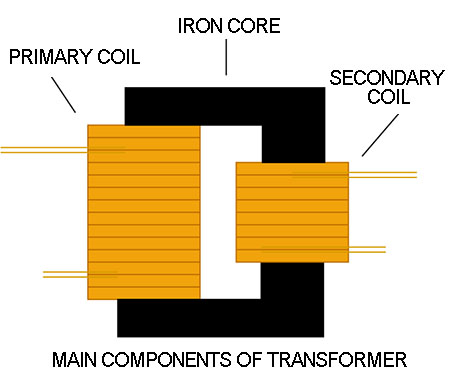
In the electronics profession, transformers can often be seen. The most common use is in the power supply module as a voltage conversion and isolation:
①: Transformation can be divided into two types: step-up and step-down. Most switching power supplies are step-down. Such electronic products are usually used in desktop power supplies, laptop adapters, mobile phone chargers, TV power supplies, rice cookers, refrigerators, induction cookers, power supplies, etc. These are AC inputs that pass through a rectifier bridge and large capacitor rectifier filtering to obtain a high-voltage DC.
②: Boosting is generally used in inverter power supplies or DC-DC lines, with emergency power supplies, and the battery 12V is converted to 220V output for power supply equipment.
③: The isolation of high-frequency switching transformers is a safety requirement to ensure the safety of electrical equipment. When AC input, the switching transformer must have a safe distance to achieve isolation between the primary AC input and the secondary power supply. The primary winding of the transformer is isolated with insulating tape, and the primary and secondary sides of the skeleton are isolated. AC passes through the human body and forms a loop with the earth, causing a danger of human conduction. There are high-voltage tests on transformers, generally requiring 3KV.
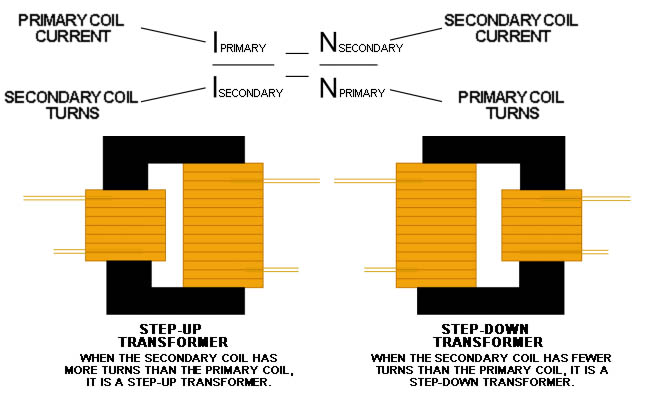
The current relationship between the primary coil and the secondary coil:
When the transformer is running with a load, the change in the secondary coil current will cause a corresponding change in the primary coil current. According to the principle of magnetic potential balance, it is deduced that the current of the primary and secondary coils is inversely proportional to the number of coil turns. The current on the side with more turns is smaller, and the current on the side with fewer turns is larger.
It can be expressed by the following formula: primary coil current/secondary coil current = secondary coil turns/primary coil turns.
The coil materials of the transformer include enameled wire, three-layer insulated wire, copper foil, and copper sheet. Enameled wire generally uses multi-strand twisted wire. The advantage of multi-strand twisted wire is to avoid the skin effect of copper wire, but multi-strand twisted wire may cause noise. Three-layer insulated wire is used in transformers with insufficient safety distance or small skeleton area, and copper foil and copper sheet are used in high-power transformers.
The winding method of the coil can improve the EMI of the transformer, especially in low-power flyback power supplies. Coil winding and shielding are very important for EMI. The winding of the coil affects the leakage inductance and parasitic capacitance of the transformer, and has an impact on the transformer loss.
The difference between low-frequency transformers and high-frequency transformers:
① Transformer operating frequency
According to the different operating frequencies of the transformer, it can generally be divided into low-frequency transformers and high-frequency transformers. For example, in daily life, the frequency of industrial frequency AC is 50Hz, and we call the transformer working at this frequency a low-frequency transformer; while the operating frequency of the high-frequency transformer can reach tens of KHz to hundreds of KHz. For low-frequency transformers and high-frequency transformers with the same output power, the volume of the high-frequency transformer is much smaller than that of the low-frequency transformer. The transformer is a relatively large component in the power supply circuit. To ensure the output power while reducing the volume, a high-frequency transformer must be used, so a high-frequency transformer is used in the switching power supply.
② Working principle of transformer
The working principle of high-frequency transformer and low-frequency transformer is the same. Both work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, but in terms of manufacturing materials, the materials used for their cores are different. The iron core of the low-frequency transformer is generally made of many silicon steel sheets stacked together, while the iron core of the high-frequency transformer is made of high-frequency magnetic materials.
③ Transformer transmission signal
In the DC voltage-stabilized power supply circuit, the low-frequency transformer transmits a sine wave signal. In the switching power supply circuit, the high-frequency transformer transmits a high-frequency pulse square wave signal.
The main functions of the transformer are: voltage conversion; impedance conversion; isolation; voltage stabilization (magnetic saturation transformer), etc. Transformers are used in almost all electronic products and are an indispensable part. The principle of the transformer is simple. According to different usage occasions and different uses, the winding process of the transformer will also have different requirements.
15 years of professional electronic components manufacturer
Post time: Oct-17-2024


