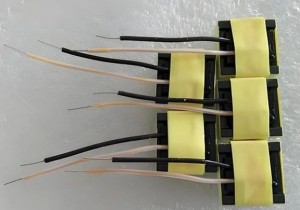
Flying wires, the windings that lead from the top of the transformer, are often insulated and sleeved.
Many people can’t help but have a question: why does the transformer have flying leads?
First of all, the transformer design flying wires, is to meet the safety requirements. Generally speaking, transformers do flywire, are secondary. Some transformer skeleton is not a safety skeleton, can not meet the safety requirements, if the secondary directly hanging on the skeleton PIN feet, certainly can not pass the safety certification. The use of flying wires, it is easy to achieve this purpose.
In order to reduce the space occupied by the transformer board, on the PCB, the transformer primary and flying wires, often also slotted, increase the distance between the two, in order to meet the safety requirements, reduce the purpose of the PCB. This is for the finished product high-density, small volume, has an important role.
Secondly, the secondary output current is large, thick wire diameter, the use of flying wires to facilitate the realization of the process. For insulated wire, hardness is very large, especially more than 0.7mm wire diameter, through the casing hanging PIN is more difficult, but also easy to cause winding PIN foot skewed, after soldering higher than the skeleton pivot, false welding and other issues. Transformer using flying wires, you can basically avoid the relevant problems.
Third, flying wires can be used to increase the transformer PIN feet. This is more common in the skeleton products, but also some of the secondary winding is more, the existing skeleton PIN number is not enough to use the case, through the flywire can be achieved to increase the number of PIN purpose.
However, it is worth noting that, despite the advantages of flying wires, but there are some problems:
If there are flying wires in the transformer, fully automatic winding of the wire package will become more difficult. Since the flying wires are not fixed at the beginning and end, even if semi-automatic winding, compared to the full PIN transformer products, the efficiency will be reduced.
In terms of testing, the existence of flying wires requires the addition of extra test fixtures to ensure the smooth running of the test. In order to facilitate PCB insertion, transformer flying wires, but also need to be processed into a certain shape, will lead to the entire transformer production process becomes more complex.
For PCB factories, the presence of transformer flying leads will greatly affect the efficiency of the transformer plug-in. Due to the flexibility of the flywire, there are often plug-ins are not in place, which can easily lead to the flywire and PCB between the existence of empty weld, false weld and other bad phenomena. If the flying lead is too long, wave soldering after welding also need to cut the foot.
In addition, some of the flying wires need to distinguish between in and out of the line (often with white and black casing), in order to avoid flying wires plug-in plug-in reverse, resulting in abnormal output.
In summary, the transformer flying wires can be easy to meet the safety requirements, facilitate the realization of coarse wire diameter process, increase the number of PIN, but the existence of flying wires, but also lead to higher production and installation costs. Therefore, in the transformer design, the need for reasonable choice. Generally speaking, the transformer can reduce the flying wires, minimize the flying wire design.
Post time: Sep-21-2024